Sunday, January 18, 2009
Questions and answers
Responses to Queries:
Responding to Junhui's Query
Hey Junhui, for your question: Under the constraints of WMS, the adoption of the WMS seems feasible only to large companies, would this deter small-mid size companies from adopting and thus limit WMS's user range?
As to whether the product can be tracked even if it's not within the country's perimeter, it can be tracked. This is because RFID tags contain information that can link wirelessly with the Warehouse Management System(WMS). RFID tags can also be used for animal identification. Also called passive RFID technology or just simply chips you put on your pet in case he/she goes missing. Anyway, RFID tags contain smart memory and a radio transmitter. Unlike bar code reading, RFID receivers receive this information and are able to identify the item/product effortlessly based on information stored on the memory in the tag. Technically wise, RFID readers can collect information from varying distances, based on the frequency of the radio transmitter. Just for your information, low frequency RFID transmitters require the person receiving to be within 1 foot. High frequency transmitters requires readers to be within 3 feet of the item. UltraHigh frequency tags have a read range of 10 and 20 feet.
To showcase clearly the advantages of RFID technology over bar code systems, major retailers in the UnitedStates such as WalMArt and Target are in the process of testing UltraHigh frequency RFID technology. Since WalMart are the only major retailer that has set the stage and integrated RFID technology seamlessly into it's system, they are requiring 100 of it's top suppliers to have RFID tags on shipments. This effectively reflects the growing trends in using RFID technology and WalMart have set an example model.
Nowadays manufacturers have been requiring RFID tags on their pallets of goods and cases that leave their warehouse. When we talk about real time information, it means the RFID tags are able to track the products from the moment they leave the manufacturer to the point it reaches the customer. This is known as efficient tracking and tracing and more importantly, provides transparency to the entire supply chain flow. So, it is true the product can be tracked even in the transportation process, during shipment when it is out of the country. But however, ultimately it all depends on the frequency of the radio transmitter. With the popular RFID trend now, there will come a time to likely have many suppliers requiring to have RFID tags on shipments as requested by manufacturers. This technology will be developing and bring even greater benefits. Who knows, so by then whether or not the product can be detected may not be a question many manufacturers would face.
Hope this helps! :))
Responding to KangCheng's Query
Kangcheng: Under the constraints of WMS, the adoption of the WMS seems feasible only to large companies, would this deter small-mid size companies from adopting and thus limit WMS's user range?
Hi Kangcheng, good question.
It's true that there are many (particularly small-mid size) companies still continue to rely on non-commercial WMS solutions like manual and spreadsheet-based solutions to maintain warehouse business operations. Citing high upfront costs, expensive software integration and lack of knowledge as part of the main hurdles to adopt WMS.
However the mounting pressures for growing companies (supporting increased sales without increasing staff, customers demanding faster order turn-around time and warehouses out of space) have clearly reached a point where information visibility and information automation are becoming more and more important to sustaining the business. These companies will find the rising need to invest in WMS as they continue to deal with these increased pressures.
The solutions to these small-mid size companies would be that they have to find other alternatives to combat these restraints, by conducting thorough investigation and evaluation phases, and in depth research on what options are availble before making decision on wheter to invest. The vendors could also play their part by educating the public and differentiate themselves when it comes to how their solutions can be deployed, helping to overcome the hight upfront costs and expensive integrations hurdles.
The future of WMS
WMS vendors are continuously honing their products to meet client needs, seeking to offer broader suite of products in the near future, with the WMS moving away from RF and instead incorporate the use of voice controls with RFID as a way to create even faster, more efficient systems.
Here's a very useful article that contain information and dicussed everything about the WMS, do read it if you have the time.
http://it.toolbox.com/blogs/wms-essentials/warehouse-management-systems-wms-going-beyond-the-warehouse-walls-26649
Responding to Solyh's query:
Hey man!Toyota has international and domestic models of cars. International models of cars are built for export overseas, based on overseas customer demands, such as in Singapore. Depends on the different geographic locations where the cars are exported to, retailers in Singapore request for certain specifications for a particular model. Borneo motors would request for standard parts/components/features in the car based on their own research on market trends, customer demands. They request for what they want in the car, and what they would not want. By the way, toyota cars are not manufactured in Singapore because of labor costs. These cars are manufactured in probably different parts of the world, where manufacturing costs and facilities may be lower.In any case, Toyota has manufacturing plants in many continents across the world.Borneo Motors will be the sole official distributor in Singapore for Toyota cars.As to your question of how JIT works for Toyota. JIT is a strategy whereby components arrive just in time for production. Many trends nowadays are towards reducing inventory and costs. Also reduces stock out situations and this is all part of risk management. This JIT system is part of the Toyota Production System(TPS). Toyota visited Piggly Wiggly and modelled after them after observing a successful functioning JIT system. As for Toyota's JIT system, many of their vehicles are built to order. Toyota redesigned their parts of almost everything so that they could accept varying customer demands and tolerate such changes. Some parts were also reduced in numbers and types to standardize assembly items.In fact, several of their car models use the same kind of assembly components. Having their JIT has this one primary purpose: that is to have the right material at the right time and at the right place in the right quantity.
Responding to Yuanhao's Query
To Yuanhao's query: Globalizing the supply chain is an upcoming trend that many companies nowadays are moving towards to. The need for 3PL services for added value logistics services provider is essential in many businesses as they move towards trying to concentrate on their core businesses. The level of trust and confidence these manufacturers have towards the 3PL companies is one not to be undermined. Hence, many manufacturers opt to allow 3PL's to handle their non-core logistics needs.
On the other hand, such practices globalize their supply chain at the same time, for some companies the globalization is huge and something to be proud of. However, for some such globalization comes along with risks and other forms of obstacles along the way. For example, the huge and high fuel prices has deterred some companies from outsourcing in foreign countries. Global issues such as Global Warming has also raised demand for green supply chains. Despite the advantages and disadvantages of globalization, there are some companies that is able to balance between the both trade-offs and even balanced it well. Being cost-effective and yet conscious about the environment is some achievement some companies have.
Some Barriers to globalizing supply chains are that the environment may be harmed. However, some companies are still trying to be the leader in this new trend of being "Green". For example, Walmart has set the stage of this new trend, starting to work down from top management and educating employees at the lower management. This process in the hierarchy is effective, as everyone in the company is aware and plays a role. It is all basically, about having the right balance in your operations. Some occassions, there is a need to be environmentally friendly and making profits for your own company's interests may not always be the right thing. Start with the little changes and you never know how big an impact it has on you.
Please refer to the example on Walmart's case.
Hope this helps !
Here is an interesting read for your reference:
http://www.scmr.com/article/CA6627635.html
Just for your interest, we've uploaded a video on supply chain risk reduction.
Take a look, if you guys can. :)

3PL is also known as third-party logistics provider. It is said that the demand for outsourced services from logistics provider is likely to grow further in the following two years. There are several reasons for this. With globalization and intensifying competition in the industry, companies prefer to seek the opinion of professional logistics service providers and concentrate on their core business areas. In the past, companies thought they could handle all their logistics needs single-handedly, but realized this has a high impact on their concentration in their core businesses. However, now companies in the industries of electronics, automobiles and spare parts are quickly signing up with UPS for logistics services to handle their logistics needs. Just for your information, UPS stands for 'United Parcel Service' and is one of the world's largest package delivery companies. For more information, please visit: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_Parcel_Service
In short, 3PL's ( third party logistics ) execute logistics activities in an external organisation. The major advantages of outsourcing to a third party logistics provider is that a company can focus on it's core business areas, while allowing their non-core logistics needs to a 3PL company, such as UPS or DHL.
Other advantages/usefulness include:
- Reduces the conventional logistics costs.
- Handle some specialized services, especially for warehouses that requires handling of specialized services, such as delivery of temperature-sensitive products.
- Provides warehousing and transportation services customized to customer's needs and market conditions.
- Increases the speed of services.
- Globalizes your supply chain, especially if you engage a variety of third-party logistics service providers across the world.
- Allows you to concentrate on your core logistics businesses.
- Enhance supply chain efficiency.
- Improves customer service with on-time transportation deliveries.
However, constraints are evident in that 3PL logistics sector is in growth gradually and logistics service charges may be on the rise in coming years. For instance, Ceva logistics, of the leading supply chain and forwarding companies is investing huge amounts of money to tap on the increasing demand for third-party logistics services.
Public Warehouses
There is increasing demand for using public and contract warehouses. To avoid confusion, public warehouse is not a 3PL although they provide services for the warehousing company. Public warehouses typically are rented facilities of the warehousing company and is often used when the company cannot justify the costs of having their own warehouse facilities and don't want to commit to owning their own facilities.
Having a public warehouse has its unique usefulness. Many companies and manufacturers are turning to public warehouses for unique advantages it brings to companies.
They are namely:
- Flexibility
- Transportation Consolidation
- Capital Preservation
- Specialised Services
- Seasonal Demand Products
- Postponement
- Market Knowledge
- Focus
Flexibility
Flexibility of space, labor and equipment has been the primary advantages of public warehousing. The current trend now is to reduce inventory levels, hence during peak seasonal demand, public warehouses offer constant space, labor and equipment to execute logistics activities and handle stored products. With sufficient lead-time, manufacturers have the luxury of having good flexibility to increase or to reduce their allocation of warehouse space and equipment.
Transportation Consolidation
To remain in this highly competitive industry, manufacturers need to achieve significant cost savings through consolidation of their inbound materials. What is this exactly? Manufacturers are aiming to receive their inbound material and goods on a JIT(Just-In-Time) basis, and turning to public warehouses to consolidate inbound goods in a single shipment. This way, manufacturers can satisfy their different points of production at the same time, with a single consolidated shipment.
To enhance the efficiency of this trend, manufacturers are developing programs to bring public warehouses close to the point of manufacturers. Warehouses will receive larger shipments consolidated out of smaller shipments on JIT basis. With these implementations, the new trend is that public warehouses conduct quality checks on the components before delivery shipments.
Capital Preservation
Specialized Services
Seasonal Demand Products
Postponement
Market Knowledge
Focus
Public Warehouse is a cost effective solution for:
Contract Warehouse
Essentially, contract warehousing is a partnership between the manufacturer and the warehousing company. Also, can be considered a "One-Stop-Shop" Logistics Centre. As mentioned, there are unique usefulness that contract warehouses have:
- Seasonality in products
- Increase Geographical coverage
- Gain flexibility in testing new markets.
- Gain management expertise and dedicated resources.
- Reduce transportation costs. ( Full Truckloads )
Despite advantages, there are also companies that prefer to engage private warehouses and own the facilities on their own. For several usefulness:
- Manufacturing companies prefer to have a high degree of control over warehousing operations, hence having efficient warehousing and services.
- Also, they have the flexibility of changing the purpose of space into any that they might desire.
- Private warehousing is less costly than renting and manufacturing companies have more confidence in their own abilities to handle their logistics needs.
- Especially so, for retail companies handling large volumes of merchandise on a regular basis.
However, there are also constraints as to private warehouses.
- Lack of flexibility in the long term when the increased size of company will restrict growth.
- Financially, start-up costs are high and hiring labor to manage the warehouse adds to the costs too.
- To make use of mechanised handling and storage systems such as the Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems(ASRS) requires technical knowledge and is capital intensive.
We all know that an objective of warehousing is to maximise the effective use of space. EDI is ready made for a just-in-time environment. Talking about JIT systems, basically this means getting incoming goods to arrive just in time to fulfill the requirements of the production plant. The main purpose of this inventory strategy is to reduce inventory levels and lower inventory carrying costs. JIT systems helps a manufacturing plant respond quicker to customer demands. This improved customer satisfaction.
Also, to make use of JIT systems effectively, good and reliable supplier relationships is definitely a must. Having such a reliable supplier will ensure that material will be there when required to satisfy customer orders any time. Having JIT systems helps a company plan its working schedule and production lines more efficiently, knowing when will material arrive just on time. Set-up time will reduce, and there is little possibility for a stock-out situation.
More importantly, JIT systems enables a company to become more flexible in terms of production schedule and ability to satisfy customer orders.
An example: I'm sure everyone still remembers the strategy built-to-order right?
In the case of Toyota, the Japanese car manufacturer, their implementation of the JIT system not only brought them greater returns but more importantly, they had effective risk management. How do we explain this? Toyota first implemented continous quality control and redesigned every part of the vehicle to provide greater offerings and variety. The reason for this? Toyota wanted to reduce the risks of having just one standardized part for their vehicle and reduce the effects of having an order rejected. Hence, this increased their tolerance for customer demand changes. Gradually, the production lines faced less and less disruptions and this minimized inhouse inventory. With all these advantages, the adoption of JIT systems has become more common. The main advantage is that JIT is able to match supply closer to demand(in timing and quantity) so that suppliers arrive just at the time they are needed.
In short, the Just-In-Time inventory system is basically to have the right material at the right time, at the right place and in the right quantity.

DELL uses a JIT approach which minimizes inventory costs. DELL's business model is a perfect envy of many other businesses. They have a manufacturing policy of manufacturing their products as close to customers as possible. Keeping low inventory allows DELL to use up its components rapidly, hence their warehouses store less inventory, saving up space for other warehousing needs.
Here is a video clip, on how DELL adopts it's built-to-order strategy and how it incorporates this into it's warehousing operations.
However, the main problem of having JII is that suppliers are open to large supply changes. Also vulnerable to supply shocks which means that manufacturers may suddenly reduce the purchase price to suppliers. Despite, many manufacturers still adopt the JIT approach to handle inventory levels, minimize production line disruptions and customer demands variations.
Here is an interesting short clip on Bohren Inc. on Transportation Division:
Cross Docking
Cross docking is a logistics practice that is becoming increasingly recognized as an indispensable way to increase inventory speed and throughput as it bypasses the put-away process, and is used by many leading companies such as WalMart. Basically, cross docking is an operation whereby products from different incoming trailer trucks arrive at the warehouse in truckload lots. There is little and essentially no storage in this operation. Goods are immediately arrived inbound and in the large staging area close to the outbound area, value adding activities such as labeling, tracking and consolidation can be performed in the cross-docking facility. In fact, different products come together at the cross dock facility and are being sorted and combined into full shipments, ready to be delivered to final customers. In terms of adding value to customers, customers value the efficiency of truckload volumes. Such effective consolidation and performed at the highest accuracy is definitely one important strength essential in warehouses and distribution centres today.
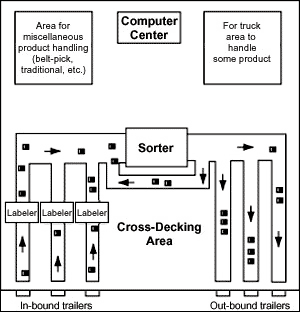
In fact, Walmart was the first to perform this operation.
Usefulness:
- Reduces inventory storage, handling and operating costs.
- Efficiency in flow and speed of goods to reach customers.
- Increases available warehouse space, for other important products.
- Streamlines the flow between supplier and manufacturer.
An important added advantage is that cross docking requires efficient and strong networking between suppliers and distribution centres. Continuous communication and reliable logistics software integration that streamlines the flow between manufacturer and supplier. An example: WalMart makes majority of it's goods, of around 85% undergo the cross docking operation. Hence, WalMart is able to offer lower prices for retailed goods because of the savings in costs using this cross docking concept that is good with a "U" flow layout. This is the main reason why Walmart is able to offer low prices for retailed products.

Okay guys, hope everyone had a good weekend doing DCM blog! After covering the introductions towards trends and challenges facing warehouses and distribution centres in the previous post,
We're here to provide you with a deeper insight into the actual trends, challenges, usefulnesses and also not to mention, the constraints present!
Technology in Our Industry..
- Electronic Date Interchange(EDI)
- Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
EDI
The importance of computerisation has not gone unnoticed. In this post, we will talk about EDI in warehousing operations, and it's usefulness and constraints. EDI stands for Electronic Date Interchange. This is a standard form of data format that can be readable between a company's computer system and another company's computer system. For warehouses to become 'information warehouses', the use of EDI technology is essential. Although this technology is commonly used, however we feel it is a trend that can be developed further and bring even greater benefits in the future. This 'paperless' technology of transmitting information flow and recording data electronically has the following usefulness.
Usefulness:
- EDI prevents errors, such as shipping and billing errors.
- Time is saved as transactions are nearly instantaneous and computers instead of human manpower is involved.
- Precious time is saved as transactions and data can be stored information into the system.
- Speed in receiving information from trading partner.
- EDI can become an important component in Just-In-Time systems.
- Production can become better scheduled.
- Data needs to be input only once into the system.
- Money can be saved by reducing the amount of paper used.
WMS
The Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), a sophisticated tool, has grown through time along with the trends of warehousing/distribution centres. It was build initially as a system to control movement and storage of materials within a warehouse, now the role of WMS is expanding to include light manufacturing, transportation management, order management, and complete accounting systems. Warehouse management systems have typically been associated with larger, more complex distribution operations. Small, non-complex distribution facilities have historically not been viewed as candidates to utilize this costly and data intensive system. However, even smaller and midsize companies are increasingly recognizing the significance of warehouse management systems in today's environment of integrated logistics, just-in-time delivery, and e-commerce fulfillment.
WMS can operate as a sole system or as modules of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, with technologies such as the RFID, ADC and EDI implementing it.
As mentioned earlier, the primary purpose of a WMS is to control the movement and storage of materials within a warehouse. With the objective to provide a set of computerized procedures to handle the receipt of stock and returns into a warehouse facility, model and manage the physical storage facilities such as racking and pallets, manage the stock within the facility and enable a seamless link to order processing and logistics management in order to pick, pack and ship product out of the facility.
Here are some notable advantages of adopting the WMS:
1. Inventory Management
Delivering inventory visibility and accuracy.
This system helps to increase the percentage of orders that are shipped complete, thus increase customer satisfaction and offset margin squeeze.
It also allows you to identify and track inventory with sufficient scale to allocate, fill, and deliver orders as accurately as possible, as often as possible. You can view and monitor the location, condition, and amounts of all finished goods, components, and raw materials in your warehousing operation, as well as rotate your inventory while adhering to FIFO and LIFO accounting principles and considering freshness, seasonality, and other variables.
• Reduce inventory on hand
• Increase picking accuracy and order fill rates
• Improve customer service
• Ensure proper inventory rotation
• Improve inventory visibility and accuracy
2. Work and Task Management
Organizing available work and tasks to optimize productivity
Increase efficiency for high-volume fulfillment and seek to align the efforts of individuals and teams with rapidly changing work priorities.
• Improve worker and workforce productivity
• Improve order fill rates
• Increase employee retention and morale
• Accelerate throughput and velocity
3. Labor Management
Optimizing labor
This toolset increases efficiency and maximize worker performance in the warehouse. Resulting in sharp workforce planning, staffing, and execution capabilities, along with the ability to monitor direct and indirect labor and provide feedback to workers and supervisors as picking, packing, and shipping activities are completed.
• Improve labor planning
• Increase worker productivity
• Optimize fulfillment execution
• Enhance customer service
• Reduce warehouse labor resource costs
4. Cross-Docking (refer to earlier post for specific explanation)
• Avoid unnecessary holding costs
• Improve product availability
• Commingle and consolidate freight
• Increase customer satisfaction
5. Value-Added Services (refer to earlier post for more information)
Adding value to the closer point of sale.
Value-Added Services enables management to adopt postponement strategies and mass customize products at the time of distribution and fulfillment to ensure customer requests are fulfilled correctly at the lowest total supply chain cost. Achieve greater ability to accommodate changing customer tastes and product requirements, with fewer excess products, parts, and components.
• Reduce lead time to customers
• Customize products closer to the point of sale
• Reduce inventory on hand
• Reduce product obsolescence
• Improve customer service
6. Voice-Directed Distribution
Giving voice to distribution and fulfillment
Voice-Directed Distribution helps to improve distribution and fulfillment processes by utilizing advanced speech recognition technology to voice-enable order selection, replenishments, put-aways, transfers, and receiving. Workers can operate hands free without reliance on cumbersome lists, labels, and scanners-thus improving order accuracy. The result is a faster, safer, and more secure work environment for all warehousing personnel, with the chances for miscommunication virtually eliminated.
• Improve accuracy
• Increase productivity
• Enhance worker safety
• Reduce training time and support costs
• Increase throughput and velocity
Here, is a short video clip on the application of using voice technology in order picking work.
As perfect as it seems to be, the WMS still has it constraints.
Even though WMS continues to gain added functionality, the initial core functionality of a WMS has not really changed. Certainly any warehouse could benefit from some of the functionality but the benefit may not be great enough to justify the initial and ongoing costs associated with WMS. Warehouse Management Systems are big, complex, data intensive, applications. They tend to require a lot of initial setup, a lot of system resources to run, and a lot of ongoing data management to continue to run. That’s right, you need to "manage" your warehouse "management" system. Often, large operations will end up creating a new information system department with the sole responsibility of managing the WMS.
RFID
Welcome again! Okay guys, this second post will offer you an insight into the detailed specifications and information about the various trends and challenges.
In short, RFID stands for 'Radio Frequency Identification'.
To give you a good introduction to the technology of RFID and it's applications and also to facilitate your understanding, we hope this video will be a useful one. :)
This technology is very popular with many warehouses and distribution operations. As supply chain transparency becomes even more essential in our industry today, the evolution and increasing use of RFID technology could not have come at a better time. With such challenges of tracking inventory, optimizing shipping and receiving, supply chain transparency, this technology becomes even more necessary. Retailers such as Walmart and Target in the United States has set the stage and developed this RFID technology. This technology has allowed manufacturers and distributors to track inventory through the demand chain as it moves throughout the supply chain to finally, end customers. RFID provides real time and highly accurate inventory transparency, improving sales and enhancing operations at the same time.

RFID technology has many uses, namely in:
- Animal identification and tracking.
- Deployment in libraries, replacing bar codes on libary items such as books, CDs and DVDs.
- Information is read using an RFID reader.
- RFID baggage tracing at airports such as the London airport and Dubai airport.
- UHF( Ultra-High Frequency) tags are used commonly in pallets, shipping containers and truck and trailer.
Technically wise, RFID is a method of identifying an object through a wireless radio link. RFID tags contain mostly 2 parts: integrated circuit for storing and processing information and the other is the antenna for receiving and transmitting the signal. RFID tags contain unique information that can link and share information wirelessly with computer databases such as the Warehouse Management System. Data encoded on each tag can be read using a hand-held scanner. Data are transferred into the WMS and updates the database at the same time. In relation to warehouses, goods being shipped out can be tracked and traced efficiently in real time. RFID technology improves the efficiency of inventory tracking. Also, RFID is a 10 year old technology that will cause a revolution in supply chain management over the next few years.
These are the main advantages of RFID technology:
- Provide real time information about the location of a product, throughout the entire supply chain.
- Efficient track and trace.
- Highly automated.
- Offers transparency in operations.
- High speed reading and sorting.
- No line of sight is required.
- Does not require the supervision of warehouse personnel.
- Provides more unique information than a bar code can contain.
- Improvement of service levels.
- Lower possibility of product/goods loss.
RFID tags contain information on where the product belongs. The material handler will then know where to send the goods to its intended destination. A simple concept: 'the faster the goods move out of the warehouse, the more efficient the process'. RFID and Bar coding both essentially carry information about a product. However, as we move away from the era of using bar coding, RFID technology allows several individual objects within the same group to be identified concurrently. This is unlike bar coding which must be read one by one. Hence, fast simultaneous and unattended reading are the main characteristics that set RFID apart from Bar Coding. A perfect example of companies using RFID technology is Walmart. Walmart is pushing this technology aggressively to its suppliers. For instance, they require 100 of its top suppliers to have RFID labels on shipments and goods. According to Walmart, this technology helps to reduce costs. As mentioned to one of our classmates' query, there are several different radio frequency transmitters with different frequency levels.
Here is an interesting picture of how RFID chips are embedded in the cardboard of T-shirt tags.

Consider any organization that requires tracking and tracing of items that you send or receive. Would you adopt the traditional method of bar code, or RFID technology? Adopt RFID technology and you will immediately see the benefits of it. Smart distributors and retailers will make use of RFID technology for new and innovative improvements in inventory and supply chain purposes. A trend now is that there is a retailer trying out the RFID technology with inventory control. Placing RFID tags on the shelves in stores can help detect low stock items and facilitate an efficient stock replenishment schedule, identify purchasing patterns and prevent the loss of items.
However, with all the advantages and benefits we’ve highlighted so far, all is not perfect and RFID do have some disadvantages too.
- RFID is more costly as compared to Bar Code.(with a current price of 50 cents per tag)
- Also, RFID tags are prone to physical damage when exposed to environmental conditions.
- Tags are bulkier as the tags are embedded with electronic components.
- Manfacturers, companies and developers will have to design their warehouse and inventory management systems to tap on using the real time nature of RFID tags information.
- Price is still the biggest constraint to adopting RFID.
In all, RFID is a technology that we would all embrace as the stage for greater efficiency in track and trace can provide greater transparency in the entire supply chain. This is a technology that will stay and develop further in the years to come. To help in your understanding, our members have decided to post up an interesting article for your reference. Enjoy!
http://news.medill.northwestern.edu/chicago/news.aspx?id=111561

Hello again :)
If you guys remember, during the field trip, this vehicle was seen somewhere close to the inbound area near the cargo lift. AGVs are gearing up to become a standard means of material handling in our logistics industry. They are basically driverless material carriers and are mobile robots that can move materials and goods around the warehouse. AGV's find their navigation around the warehouse area with sensors. It has two kinds of sensors used: the wired sensor and wireless sensor. The wired sensor is placed somewhere below these robots AGVs and close to the ground. Navigation comes from the sensor detecting the radio frequency from the wire placed in a slot made on the ground.
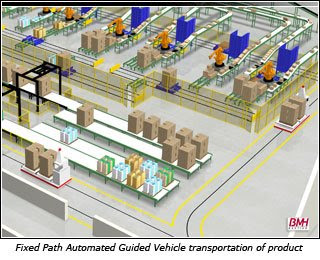
Basically, there is a fixed path which the AGV has to follow by sensing based on instructions from the central traffic controller. AGVs are able to pick up pallets from conveyors and racking. Maximising the efficient use of space is one of warehousing objectives. Hence, the adoption of mechanised systems like the AGV is commonly adopted in performing warehouse operations. Companies like Bastian Solutions are one example that has been using this vehicle in their operations. Also, some AGVs use forklifts to lift objects.
To highlight the benefits of using AGVs:
- Reduces the costs of manufacturing.
- Increases efficiency in a manufacturing system.
- Flexibility in changing routes and valuable to companies constantly changing production.
- Offer reduced labor costs and decreased downtime.
- Most importantly, they minimize the chance of damage to goods.
Vertical Carousel System

This system is increasingly being used by companies today. The carousel system is a mechanised system exist in two types: Vertical carousel system and the other is the horizontal carousel system. Vertical carousel systems operates on a different concept and delivers the desired product to the order picker. Technically, they use a series of bins mounted on a oval track and are suspended between two continuous chains.
Vertical carousel systems can be built to make use of available building height. Driven electronically, the stock is brought to the operator automatically, showcasing a part-to-picker concept. To maximise the efficiency in performing the operational areas in warehouses, in this case picking, adopting a vertical carousel system is important, as we describe it's valuable advantages to you here.
- Vertical carousel system maximises floor space and fully utilizes the cubic capacity in the DC.
- Vertical carousel system uses lesser floor space compared to the horizontal carousel system.
- Provides high speed and accuracy in order picking work. ( Enhances order picking operational area in warehouse)
- It is an ideal storage system in broken cases picking in a high throughput DC.
- Less use of manpower and manpower movement in order picking work.
- More importantly, security is enhanced as the goods are in a protected storage, somewhat like a 'consume chamber', which is not within the visibility of the order picker.
- Vertical Carousel system are put on to computer control, linking to the WMS system.
- Uses random storage location, hence fully utilizing storage space.
However, there are some constraints towards adopting the Vertical Carousel System. The set-up costs are high as the system is fully automated.

Hey guys, I can't link the video here, so if you would want visuals, you can go to this link:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qcM6kX-_FUc
Thanks!
Saturday, January 17, 2009
Trends and Challenges facing Warehouses & Distribution centres
In the past decade, warehousing and distribution operations have had to cope with a variety of emerging business trends and forces. The days of straight fulfillment operations have given way to a more complex world. Buying habits have dramatically changed for manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers and consumers alike. In the foreseeable future, companies are expected to increase material handling equipment, related software & systems to keep pace with expanding business activities. Service levels have become increasingly more demanding and mergers and acquisitions have caused distribution networks to be revamped at a rapid rate.
The functions and operations of warehouses & DCs have also changed over time. Today, processes to handle value-added services were an important part of the design, as customers are looking for distributors to take over many of the supply chain functions they once handled in-house. For example, quality control tasks, repacking, compliance documentation, labelling and kitting are some of the activities that require extra handling at the warehouse.

Basic functions in a warehouse include storage, movement and information transfer. This information transfer is essential to the efficient operation of many warehouses in today’s ever-changing industry. Just to name a few, information technology such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Automatic Data Collection (ADC) and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) are value-added advantages in our warehousing process.

EPIC
Some large retailers like Wal-Mart have set the stage for RFID to be one of the most dominating technologies in distribution in the coming years. For it has the potential to help supply chains lower operating costs, improve inventory accuracy, increase throughput, enhance product authentication, reduce inventory levels, and increase visibility. Below is a photo of workers at the Walmart Distribution Centre in the United States.
RFID will prove to become a crucial technology in the coming years for the efficiency it provides in warehouse and distribution operations. Current trends indicate the market for RFID technology will grow quickly in the next decade. We will go into details for this technology in our next few posts.
Other trends in warehousing include the outsourcing of their warehouse and distribution functions through third-party logistics providers (3PL). A 3PL provides the ability to leverage an external entity's distribution infrastructure and experience instead of internally developing and supporting logistics resources.
A growing warehouse trend is to engage the services of public warehouses. To give you all a basic idea, public warehouses offer greater flexibility in space and provide certain specialized services. Companies who want to concentrate on certain product offerings and preserve capital for other investments, prefer to tap on the advantages of public warehouses. Increasing trends show that public warehouses are moving away from their niche of being just a warehouse for storage of products, to becoming “information warehouses”.
Another growing public warehouse trend is the engagement of contract warehouses. Contract warehouses are known to provide customized logistics services. In the past, companies wanting to reduce costs concentrate on their manufacturing. Nowadays, companies outsource its logistics operations and concentrate on primary businesses.
An important point to take note of, is of course the implementation of different kinds of value-added services. Companies that used to offer only limited offerings are expanding their service capabilities and value adding roles.
Just to name a few services include:
- Transportation consolidation
- Product Mixing
- Service
- Contingency Protection
- Smoothing
- Postponement
The importance of fulfilling customer service levels, efficiency and speed in performing operational areas in both warehouses and distribution centres cannot be underlined and these are trends and challenges that companies are facing and adapting to. Computerising the warehousing operations has been developed in requisitions, stock locations, open and back orders as well as working standards. "Paperless" warehouse picking has also become increasingly popular and the impressive thing is that, such computerisation has the benefits of improved pick productivity, reduced error, improved throughput, better work satisfaction, improved customer service levels and most importantly a competitive edge.
Through such trends, comes the challenges of living up to these wonderful advanced technologies in our world today. Nowadays, warehouses and customers alike expect zero tolerance for errors. The expectations of having the right product at the right time and at the right place are becoming more evident and this is definitely essential. The challenge comes in the integration of our supply chain and how well this integration is managed by everyone in the supply chain. For example, postponement strategies, cross docking, efficiency in order picking and good productive storage layout and systems planned.
To elaborate, order picking rates can be enhanced with the use of mechanised systems such as the Vertical or Horizontal Carousel Systems. Just for a brief idea, this carousel system was witnessed at the ALB field trip we went to two months ago. It provides good order picking rate, uses a well developed part-to-picker concept.
The adoption of JIT practices is one of the key measures that allows the right product to be at the right place, at the right time and finally, at the right cost. The postponement strategy and cross docking will be covered on in our next entry. Stay tuned!
Next on, we move on to trends and challenges with specific details, their usefulness and constraints.
